Aws Services
If you're new to AWS (or cloud concepts in general), or if you are studying for an AWS certifications, there is always a chapter explaining the concept of services.
This is really what cloud is all about.
AWS Services
- AWS stands for Amazon WEB Services, and really these services are accessible through the web.
- Since these services are already deployed for you, it is easier and faster using it:
- no need to deploy hardware (e.g no servers, no load-balancers, no routers, no FWs..)
- no need to deploy software (no databases, no Linux/Windows/OSx, no Kubernetes...)
- no need to care for geographic presence (it is easy to make it work around the globe)
- The basic usage pricing scheme is pay as you go, so you can start/increase/descrease/stop almost every service you use.
IT CAN BE CHEAPER in many cases (but not always)
but it is certainly simpler to implement and use: AWS is doing some of the work for you. - We're accessing these services by contacting AWS vi WEB API (Application Interface):
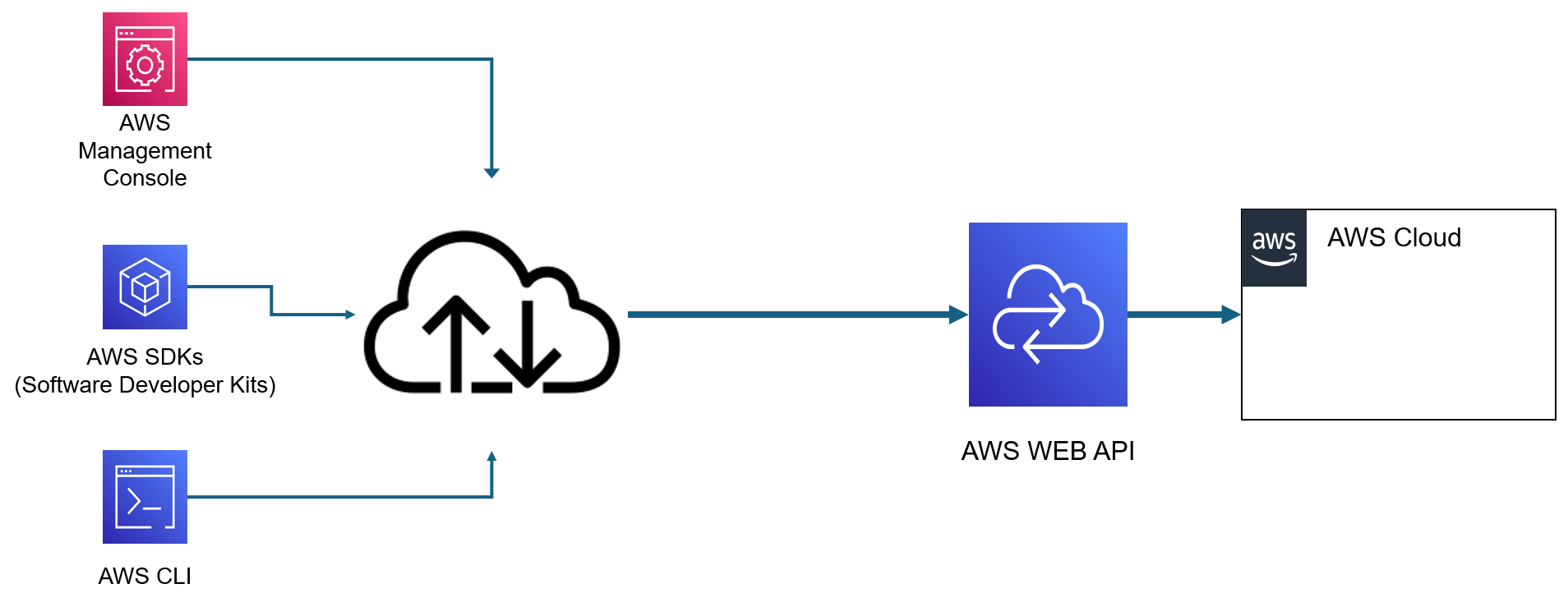
What Services
- How many AWS services are there?
As of April 2024, most sources stil stick to that "more than 200 services".. phrase - There are many categories:
- Compute: AWS App Runner, Batch, EC2, EC2 Image Builder, Elastic Beanstalk, Lambda...
- Containers: Elastic Container Registry, Elastic Container Service, Elastic Kubernetes Service...
- Database: Amazon DocumentDB, DynamoDB, ElasticCache, RDS, ...
- Machine Learning: Amazon DodeGuru, AWS DeepRacer, Amazon Lex, Amazon Polly...
- Storage: AWS Backup, EFS, FSx, S3, S3 Glacier...
- ...
Managed and UnManaged Services
- Sometimes, AWS takes care about everything until the virtualization point.
That includes physical data center, cooling, power, physical servers and hypervisors. - In these cases, your responsibility as a customer starts with the OS you would run on the virtual machine.
This is the case of unmanaged services.
AWS refers to that as the Shared Responsibility Model - The case(s) for managed services are where the barrier between AWS and the customer is placed higher, so AWS does more for you:

Server based and Serverless Services
- The concept is close to what we were discussing in the last section:
- If you don't think about the server(s) that is doing the work for you (its IP address/hardware/OS etc), then you are using a serverless service.
- S3 storage is a good example: you know some wervers are part of that service, but you don't know how many, their specific IP address etc.
- RDS is an example of a server oriented service:
- It is true that AWS is responsible for the DB software (so patching it, installing it etc), but...
- ..you are aware of a specific server type involved (so you know the specific subnet, the IP address, hardware type etc.)
Learning AWS is learning about AWS services.
Enjoy!